The RS-232 interface is one of the most enduring and widely used technologies in the history of electronic communication. While it may not be as flashy or accelerated as some modern communication interfaces, its reliability, simplicity, and versatility made it essential in various applications.
With its roots in the 1960s, RS-232 was originally designed for computer communication with peripherals, like printers and modems. By addressing the compatibility challenges of the era, RS-232 became a widely accepted standard. However, its applications have expanded, making it relevant in areas like automation, health care, and telecommunications.
RS-232 plays a critical role in achieving consistency and reliable performance in everything from industrial machinery to scientific instrumentation. This guide will tell you everything you need to know about RS-232 interfaces, how they work, and why they are popular choices for reliable data transfer.
What Is RS-232?
RS-232, short for “Recommended Standard 232,” is a standard protocol for serial communication. It defines the communication method between two devices, typically data terminal equipment (DTE), such as a computer, and data circuit-terminating equipment (DCE), such as a modem.
The standard specifies multiple parameters, including voltage levels, signaling rates, and the physical connector layout. Unlike some modern communication protocols that require complex setups, RS-232 focuses on simplicity. Its design ensures easy implementation, which is one of the reasons it continues to be a popular tool.
How RS-232 Works
RS-232 transmits data over a dedicated cable using a series of voltage signals. It transmits this data in a serial format, meaning it sends the information one bit at a time. Communication occurs over two primary lines: transmit (TX) and receive (RX). TX is responsible for sending data, while RX is responsible for receiving data.
Additional lines may control signals such as request to send (RTS) and clear to send (CTS), depending on the specific implementation of RS-232 if employing hardware flow control. Voltage levels in RS-232 are distinct, with positive voltages representing one binary state (logic 0) and negative voltages representing the opposite state (logic 1). This differentiation reduces noise interference and ensures clear communication.
Key Features of RS-232
An RS-232 has several distinct features, making it a reliable choice for serial data transmission across various systems. Here are its key attributes:
Point-to-Point Communication
RS-232 establishes direct communication between two devices, ensuring a straightforward and uncomplicated connection setup. This makes it effective for transmitting data across devices without complex networking arrangements.
Support for Long Cable Lengths
The standard supports data transmission over distances of up to 50 feet at standard baud rates. This capability makes RS-232 suitable for applications where devices are far apart, minimizing the need for immediate proximity.
Compatibility and Versatility
RS-232 is cross-compatible, enabling it to interface with various hardware and systems.
Wide Range of Supported Baud Rates
RS-232 can handle a variety of baud rates, from low-speed to moderate-speed data transmission, making it adaptable to different performance requirements.
Low-Cost Implementation
With its simple design and widespread acceptance, RS-232 offers a cost-effective solution for serial communication.
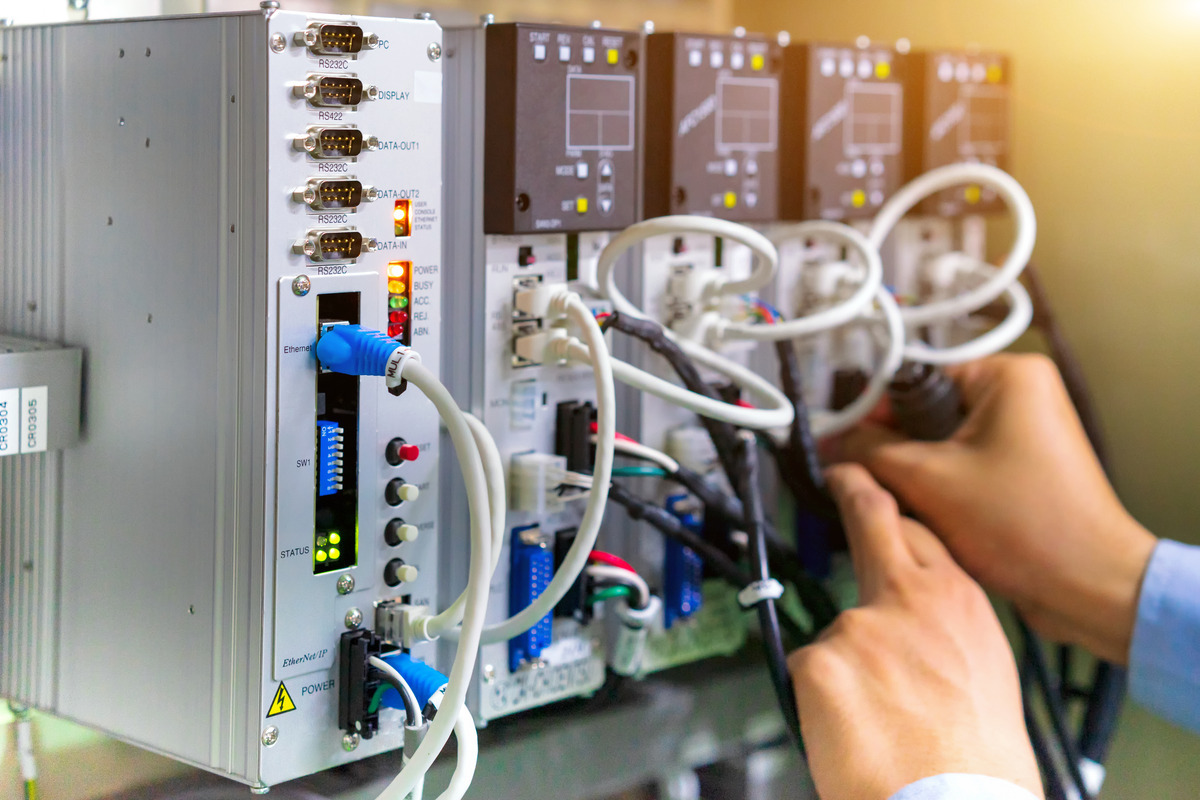

Applications of RS-232
RS-232 is a versatile and enduring communication standard with applications across various industries thanks to its simplicity, reliability, and adaptability. Below are some of the key areas where a quality RS-232 interface excels.
Industrial Automation
RS-232 plays a vital role in industrial settings in connecting programmable logic controllers (PLCs), human-machine interfaces (HMIs), and other automation devices. It enables real-time data exchange and facilitates seamless machinery control.
Health Care and Medical Devices
The health-care sector relies on RS-232 to connect critical medical equipment such as patient monitoring systems, diagnostic devices, and imaging machines. Its reliable communication ensures the consistent transfer of essential data for accurate diagnostics and patient care.
Scientific and Laboratory Instrumentation
Laboratories often employ RS-232 interfaces to connect scientific instruments such as spectrometers, chromatographs, and balances. This allows for efficient control of experiments and the collection of precise measurement data.
Telecommunications
RS-232 remains a key interface for telecommunications devices like modems, routers, and network equipment. It is essential for initial setup, diagnostics, and configuration, providing a dependable solution for managing communication systems.
Embedded Systems
RS-232 is popular in embedded systems due to its straightforward design and ease of implementation. It is a common choice for microcontroller communication, data logging, and system debugging.
Aerospace
The aerospace industry often employs RS-232 to interface with avionics equipment, test systems, and ground control systems. Its ability to function in demanding conditions makes it a dependable choice for mission-critical applications.
Common Challenges With RS-232
RS-232 communication, while reliable and widely used in many industrial and legacy systems, comes with some challenges. RS-232 is susceptible to electrical noise and electromagnetic interference, particularly in harsh industrial environments, potentially leading to corrupted data transmission. The standard’s single-ended signaling design makes it less resilient to these interferences than differential signaling methods.
Another common challenge is the limited compatibility with modern devices, as newer technologies often prioritize USB, Ethernet, or wireless communication protocols, making RS-232 less common in consumer and cutting-edge applications. Despite these challenges, proper attention to grounding, shielding, and cable quality can mitigate many issues while maintaining reliable communication.
How To Set Up an RS-232 Connection
Setting up an RS-232 connection begins with understanding the equipment involved. Follow these basic steps:
- Identify the DTE and DCE devices. Determine which device will act as the transmitter and receiver.
- Select the appropriate cable. Ensure the cable length and type match the requirements of your application.
- Match settings on both devices. Configure parameters such as baud rate, parity, data bits, and stop bits to be identical between devices.
- Connect the RS-232 cable securely to the devices. Double-check the connection of the correct pins.
- Test the connection. Run diagnostic tools or software to confirm that data transfers as expected.
The Future of RS-232
RS-232 may be an aging technology, but it is far from obsolete. Many industries depend on RS-232 for its stability and integration with legacy systems. While modern interfaces offer faster speeds or greater connectivity options, RS-232 remains invaluable where simplicity and reliability are paramount.
These devices will likely coexist with newer technologies, especially in niche applications and industries requiring low-cost, dependable communication. It serves as a reminder of the power of simplicity in communication protocols and proves that the old ways still have a place in modern technology.
With its simple design and widespread availability, these devices remain essential for stable data transfer. Learning everything you need to know about RS-232 interfaces, like key features and how they work, will equip you with the knowledge to utilize this enduring technology effectively.
While newer technologies may offer more advanced features, RS-232 remains relevant due to its cost-effectiveness, simplicity, and compatibility with legacy systems. Its future appears bright as it finds applications in various industries where dependable communication is crucial.

